Introduction
ABS is known as an anti-lock braking system. EBD is an electronic brake distribution system. BA is known as the braking system. These are all cutting-edge car-breaking technology. Almost all of us are aware of such terms but only a handful knows what exactly they mean and how exactly they strengthen the safety department of a vehicle. Their functionality is completely different from that of regular brakes and these are considered much safer for the occupants. These features are present in several vehicles from the hatchback, compact SUV, and multi-purpose vehicle segments of the domestic market.
ABS:
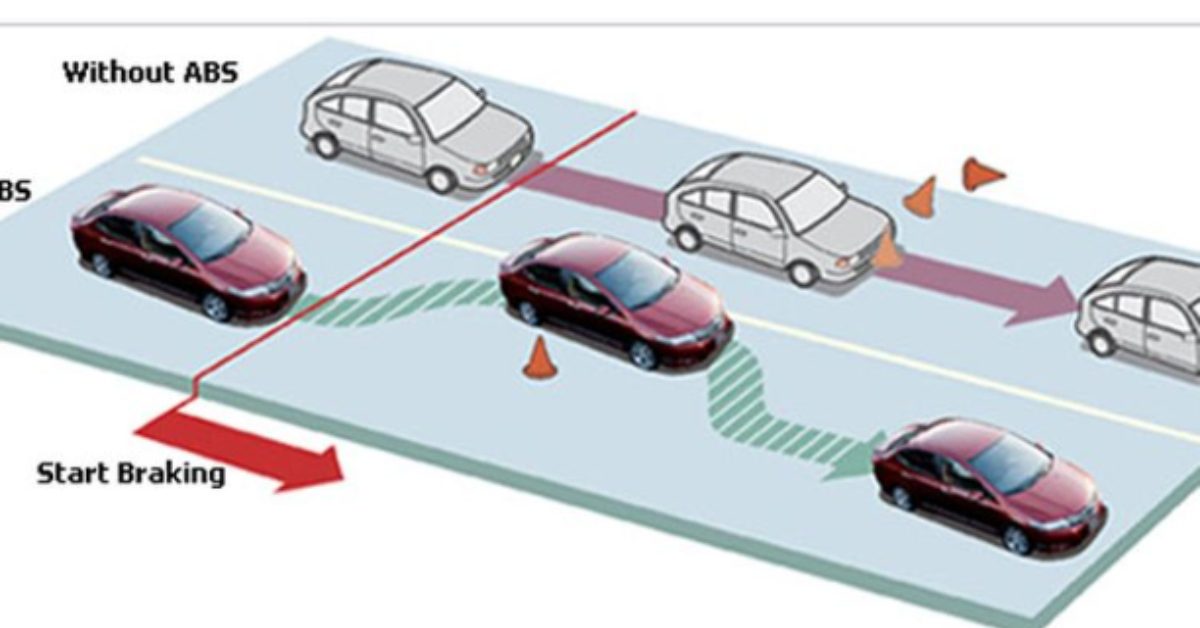
ABS prevents the wheels of the car from locking up when the car applies the brakes suddenly in certain situations. This type of brake allows the driver to have complete control of the car’s steering when maximum force is applied to the brake pedal. Generally, when the driver suddenly applies brakes on a moving car to a high probability that the wheels will get stuck due to the sudden brake force and slide on the road. This happens because the momentum of the velocity of the car is carried by it and the wheels are unable to it into rotational motion due to the brakes.
ABS or anti-lock braking system is a piece of safety equipment that prevents the wheel of a vehicle from locking up under emergency panic or harsh braking conditions. When braking on wet surfaces during rain you tend to depress the brake pedal to its full limit and eventually end up locking the wheels. At this point, your car starts sliding straight without directional control. The situation becomes worse when all this happens uncontrollably. The loss of grip may result in the driver losing control over the steering of the vehicle.
How did the ABS work?
The anti-lock braking system has four main components.
- Speed sensors:
Speed sensors monitor how fast the wheel is rotating.
- Valves:
Valves allow to block and release pressure on the brakes.
- Pumps:
Pumps are filled with hydraulic fluid and apply pressure to the brake drums on demand.
- Controller:
The electronic control unit ECU is the brain of ABS and uses data from sensors to determine whether to pump the brakes or not.
The speed sensors are located on the wheels that monitor the speed of each wheel. When sensors detect that your car’s tires begin locking up. The electronic control unit reads the signal from each sensor and sends the signal to the valves of the respective wheel. Then the valves rapidly apply and release the brakes automatically to keep your tires from skidding and help keep the driver in control of the vehicle. If speed sensors detect that the speed of any of the wheels is reducing drastically compared to others. The ECU sends the signal to the valves of the respective wheel to reduce the brake pressure and the valves get closed.
After this, the wheels start to accelerate again and the signal is sent to the ECU one more time which in turn sends the signal to open the valve and increases the brake pressure hence brakes are applied. The cycle repeats itself until the application of brakes becomes normal. So essentially ABS works in three stages. The brake pedal is pushed while the sensor detects skidding or locking ABS pumps the brakes. In a car equipped with ABS what mostly happens is the system applies the brakes in small pulses to prevent sudden brake locking that is why you can feel vibrations and juddering at the brake pedal when ABS is activated. When you feel or hear the ABS vibrating continue to firmly press and hold the brake then steer to safety.
EBD:
EBD stands for electronic brake force distribution. While ABS is the overall automotive braking technology and EBD is just a part of the overall system. However, both these elements are equally important in reinforcing the safety department of the vehicles. The EBD is responsible for distributing the braking power to all wheels of the car. Also helps in regulating and applying the braking force needed to each will according to the road condition vehicle’s load and speed. The EBD ensures how much braking force is needed by each wheel and then applies the same to achieve the most suitable braking impact.
How does the EBD system work?
When a car slows down its weight shifts forward in a front-engine car EBD comes in. EBD and ECU determine the slip ratio of each of the tires individually. If the ECU notices that the rear wheels are in danger of slipping it applies less force to them while maintaining or if necessary increasing the force applied to the front wheels. EBD is also useful when the car is braking while driving around a corner while turning the outer wheels of the car rotate more quickly than the inside wheels. If too much brake force is applied to the inner wheels they can lock causing the car to oversteer and go out of control.
EBD can sense the slippage of the inner wheels and reduce the brake force on those wheels without reducing the force on the outer wheels. Several vehicles such as HONDA, VOLKSWAGEN, and NISSAN cars have these features as standard. The same can be inquired through the HONDA or NISSAN dealers while purchasing the particular models.
An EBD system makes use of three components:
- Speed sensors
- Brake force modulators
- Electronic control unit
The speed sensors not only calculate the speed of the car but also calculates the speed of the engine. One of the scenarios can be that the speed of the wheel might not be the same as the speed of the car. Such situations can lead to wheel skidding. The speed sensors calculate the slip ratio and relay it to ECU (it is a small chip that collects the data from the speed sensors in each wheel and uses the data to calculate the slip ratio).
The slip ratio is the difference between the speed of the car and the rotation of the tire. Once the slip ratio is determined. It makes use of the brake force modulators to keep the ratio within the limits of brake force modulators. It is the job of these modulators to pump brake fluid into the brake lines and activate the brake cylinders. The brake force applied on each will can be modulated. All these three components work in tandem and make the EBD work and save your day every time you brake hard.
BA:
It is also known as emergency brake assist. EBA is another piece of car braking technology. It is responsible to assist the driver in emergency stop situation. The braking system will more swiftly when there is sudden braking if it is equipped with the BA feature. This feature aimed at making sure that the brakes are applied in case of an emergency if the driver is unable to respond quickly enough. This happens a lot that in case of sudden braking. The driver is not able to press the brake pedal fully. However, an average driver isn’t actually fast enough for a situation like a situation like this where a mile- second of delay can translate to CA strophe.
With the brake assist the electronic sense the speed and force with which the driver pressed on the brake pedal and apply additional pressure on the pedal for full braking. Travel sensor attached to the brake pedal that allows the brake assist system to detect when the driver attempts an emergency stop and regardless of the amount of pressure actually applied. It will apply maximum braking force until the car is brought to a stop.
Some more braking assistance systems can detect a sudden liftoff from the gas paddle or receive imminent crash warnings from radar or camera guided crash detection systems and prime the braking system.
You can also see this: ADAS System Works in the car.
How brake assist (BA) works?
This system works with the three main components
- Accelerator sensor
- Brake sensor
- Electronic control unit (ECU)
During such event when driver lifts off foot from accelerator and presses brake pedal. The same actions are performed even in the case of emergency braking but with the greater intensity. ECU measures this intensity with the help of inputs from accelerator and brake sensors and determines weather the driver has encountered an emergency. If it is found that the braking is due to an emergency then ECU orders the brake booster. A component of brake system that can control pressure braking to apply more pressure on brakes. So that vehicle could be brought to a stop early. The system takes care that the pressure applied is always optimum. Undoubtedly, this system is very useful in reducing the stopping distances. During emergencies as it applies optimum brake force almost instantly. Also this system helped saving many lives by avoiding accidents.