With increased interest in renewable and sustainable energy systems and course electric-powered vehicles, and solar-powered cars have come to the fore. Many automobile companies are working toward making solar car works and the technology could well change the future of the automotive industry.
While solar has undergone a comparable revolution in photovoltaic development a mass-produced solar car has yet to hit the market anywhere in the world. The term solar panel vehicle generally describes any vehicle with solar cells integrated into its design known as solar electric vehicles.
Solar-powered vehicles are electric vehicles that use photovoltaic cells to convert energy from sunlight into electricity. These vehicles can store some solar energy and batteries to allow them to run smoothly at night or in absence of direct sunlight. If used on a large scale solar-powered vehicles not only help with environmental pollution but also with noise pollution.
Many prototypes of solar-powered cars are currently in development and some are even produced. Both large and small automakers are involved in developing hybrid solar cars. According to estimates, the solar vehicle market could reach 689 billion dollars by 2027. Automobile companies are already working on ways to capitalize on the idea with interim technology such as solar roof panels for charging batteries and internal systems.
Car with solar panel roof:
Solar panels can generate enough electricity to charge 30 to 60 percent of a car’s battery with six hours of daily charging. This adds around an extra 800 miles annually. In Japan, the TOYOTA PRIUS PRIME is available with a solar roof to add up to six kilometers of driving range per day.
However, this Tech is unavailable in the US as the materials used do not pass U.S rollover tests. In NISSAN leaf the company released its first solar roof car in 2010 well ahead of the pack. The vision of sun-powered transportation dates back at least to 1955 when general motors company displayed a 15-inch toy car outfitted with solar cells at a CHICAGO trade show.
Nearly, three decades later two men teamed up to drive an oddly shaped solar-powered vehicle from Perth to Sydney according to the national museum of Australia. The low-slung bathtub on wheels averaged about 19 miles an hour taking nearly three weeks to complete the roughly 2,500-mile journey. Within a few years, solar vehicle competitions were cropping up in Australia and other countries.
Advantages of solar car:
- The benefit of solar-powered vehicles is that they don’t require fuel and have a low cost of maintenance.
- The solar roof will capture sunlight continually whether the car is moving or stationary and can run longer on the same battery.
- This requires fewer charging stops and will get you faster from point A to point B.
- Solar energy will never run out and it is free.
- Drastic reduction of air pollution due to the absence of residual pollutants like carbon monoxide nitrous dioxide etc. It also reduces noise pollution as solar car works are noiseless from a user perspective all you need is a regular power outlet combined with the sun no need to wait for charging infrastructure again creating a scalable solution great for drivers who travel short distances in sunny climates.
Disadvantages of solar car:
- The first and foremost disadvantage is the solar panel itself. The current commercially operated solar panels that we use have only around 20 to 35% efficiency.
- Hence to power a solar car works we would need a lot of extra space for solar cells.
- Weight and cost.
Solar panels are not cheap and they are not weightless either packing the car’s body with solar panels means that you are adding a lot of weight and cost to the car. Solar films have been developed that are much lighter than panels although they are less efficient at the same time and when you factor in the weight of the battery the idea of solar-powered cars seems less and less feasible in the real world.
- On a clear day if consider a highly efficient 32 square foot PV panel can generate roughly eight kilowatt hours of energy per day which means you would only get around 25 miles of range out of a normal complement of panels.
- Poor weather conditions driving conditions improper positioning of the panels and accumulation of dirt would likely make your solar car works struggle to reach this figure.
- The earth’s curvature can also affect the efficiency of solar panels it means only a small area of the earth’s surface directly faces the Sun at any given time.
- Everywhere else solar panels are tilted away from the sun somewhat limiting their ability to harvest energy. Additionally, solar-powered cars aren’t 100% eco-friendly.
- If you look at the way batteries and solar cells are made especially how the minerals used are mined from the earth it becomes clear that each vehicle comes with its share of carbon footprint.
- As long as the sun shines you could drive at a constant speed of 62 miles per hour in ideal conditions. Those solar panels could also charge a 75-kilowatt hour battery pack in 6.25 hours allowing you to keep driving at night. However, real-world conditions aren’t ideal.
- Only about 55% of solar energy makes its way to the earth’s surface the rest is reflected away or absorbed by the atmosphere.
Working principle of solar car:
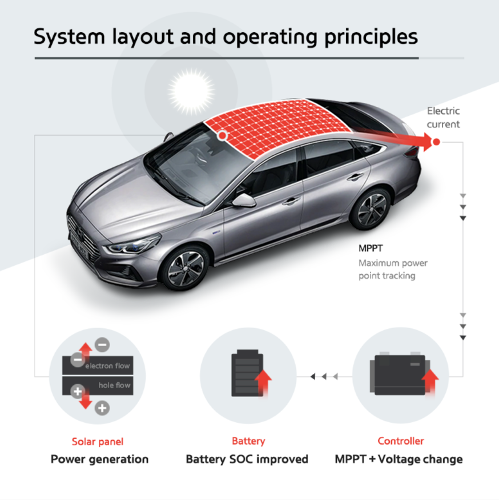
Solar cars have solar panels custom designed to be mounted on the surfaces receiving maximum sun rays which is generally the rooftop. A solar panel allows photons or particles of light to excite electrons generating a flow of electricity.
Solar panels are made up of many smaller units called photovoltaic cells that are linked together. The elements used in the making of PV cells are most commonly silicon alloys of nitrogen gallium and indium.
All of these elements can retain light and then release it in the form of rapidly moving electrons which help in generating a flow of electricity. Each PV cell is made of three layers much like sand which.
The two outer layers are made of silicon that acts as a semiconductor. The silicon is mixed with other materials usually phosphorus and boron to give each slice a positive or negative electrical charge. This creates an electric field at the junction between the two layers. Phosphorus adds extra electrons into the slice which makes the top layer a negative charge and boron makes the bottom layer a positive charge by reducing the number of electrons.
These elements have a natural retentive property that allows them to absorb the light energy from the solar rays. When a photon of sunlight knocks an electron free the electric field will push that electron out of the silicon junction. Metal conductive plates on the sides of the cell the electrons and transfer them to wires. At that point, the electrons can flow like any other source of electricity, the retained energy then releases in the form of free-moving electrons into specially designed storage sections. We refer to this storage facility as batteries.
They comprise special elements like lithium-ion and nickel-cadmium etc. These batteries can convert free electrons into usable energy to power the vehicle engine
. The specialty of these batteries is that we can use them repeatedly to power a vehicle and we can do it by recharging them using solar energy. The best aspect of these solar cars is their ability to constantly keep recharging their battery even when parked idle under sunlight. Therefore, this reduces the cost of operation of a car to almost negligible.
Solar-powered cars:
Light year one:
Light year one is the first car capable of talking us long distances while powered only by the sun which consumed two to three times less energy than any other electric vehicle on the market today which results in an exceptional range of 450 miles.

However, the overall achievable yield strongly depends on the driving patterns of individuals. According to light year, their car uses83-watt hours per kilometer and accelerates from 0 to 60 miles per hour in 10 seconds. This car has around 1000 individual solar cells across the car that ultimately add 30 to 40 miles of range per day in summer.
The solar cell modules can charge the car’s battery with up to 7.5 miles of range an hour. These solar cells are 20 percent more efficient than the solar panels you can buy for your home. Aside from its solar power recharging the car can also be charged at charging stations and at regular outlets. Only with the sunlight light year, one can charge at 7.5 miles per hour with 60 kilowatts fast charging. The car’s efficient charging allows it to charge up to 350 miles per hour.
Aptera sol:
Aptera sol is solar powered three-wheeler EV and a sight for sore eyes. As per Aptera motors, the APT aerosol is a new three-wheeler EV that will have a range of up to 1000 miles with a full charge. The two-person vehicle boasts a solar panel roof array and can provide up to 45 miles of range per day.
The vehicles charge with their solar panels in park mode. The solar EV can go from zero to 60 miles per hour in 3.5 seconds while an all-wheel drives 150 kilowatts and can go from zero to 60 per hour in 5.5 seconds in front-wheel drive and it has a top speed of 100 miles per hour.
Sion:
Sion is a hybrid electric vehicle made by german startup sono motors that charges itself using solar energy. The company claims this is the first commercially available hybrid solar electric vehicle. The car can go up to 155 miles on a single charge and adds around 21 miles of charge per day via it solar panels. It is equipped with 248 solar cells that are integrated into its body.

2 Responses
I congratulate, the remarkable answer…
It seems to me it is excellent idea. Completely with you I will agree.